By Alex Jordan, University of Wisconsin-Stout
Every week, millions of Americans toss their recyclables into a single bin, trusting that their plastic bottles, aluminum cans and cardboard boxes will be given a new life.

But what really happens after the truck picks them up?
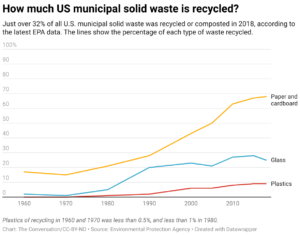
Single-stream recycling makes participating in recycling easy, but behind the scenes, complex sorting systems and contamination mean a large percentage of that material never gets a second life. Reports in recent years have found 15% to 25% of all the materials picked up from recycle bins ends up in landfills instead.
Plastics are among the biggest challenges. Only about 9% of the plastic generated in the U.S. actually gets recycled, according to the Environmental Protection Agency. Some plastic is incinerated to produce energy, but most of the rest ends up in landfills instead.
So, what makes plastic recycling so difficult? As an engineer whose work focuses on reprocessing plastics, I have been exploring potential solutions.
How does single-stream recycling work?
In cities that use single-stream recycling, consumers put all of their recyclable materials − paper, cardboard, plastic, glass and metal − into a single bin. Once collected, the mixed recyclables are taken to a materials recovery facility, where they are sorted.

First, the mixed recyclables are shredded and crushed into smaller fragments, enabling more effective separation. The mixed fragments pass over rotating screens that remove cardboard and paper, allowing heavier materials, including plastics, metals and glass, to continue along the sorting line.
Magnets are used to pick out ferrous metals, such as steel. A magnetic field that produces an electrical current with eddies sends nonferrous metals, such as aluminum, into a separate stream, leaving behind plastics and glass.
The glass fragments are removed from the remaining mix using gravity or vibrating screens.
That leaves plastics as the primary remaining material.
While single-stream recycling is convenient, it has downsides. Contamination, such as food residue, plastic bags and items that can’t be recycled, can degrade the quality of the remaining material, making it more difficult to reuse. That lowers its value.
Having to remove that contamination raises processing costs and can force recovery centers to reject entire batches.
Which plastics typically can’t be recycled?
Each recycling program has rules for which items it will and won’t take. You can check which items can and cannot be recycled for your specific program on your municipal page. Often, that means checking the recycling code stamped on the plastic next to the recycling icon.
These are the toughest plastics to recycle and most likely to be excluded in your local recycling program:
- Symbol 3 – Polyvinyl chloride, or PVC, found in pipes, shower curtains and some food packaging. It may contain harmful additives such as phthalates and heavy metals. PVC also degrades easily, and melting can release toxic fumes during recycling, contaminating other materials and making it unsafe to process in standard recycling facilities.
- Symbol 4 – Low-density polyethylene, or LDPE, is often used in plastic bags and shrink-wrap. Because it’s flexible and lightweight, it’s prone to getting tangled in sorting machinery at recycling plants.
- Symbol 6 – Polystyrene, often used in foam cups, takeout containers and packing peanuts. Because it’s lightweight and brittle, it’s difficult to collect and process and easily contaminates recycling streams.
Which plastics to include
That leaves three plastics that can be recycled in many facilities:
- Symbol 1 – Polyethylene terephthalate, or PET, widely used in soda bottles.
- Symbol 2 – High-density polyethylene, or HDPE, commonly used in milk jugs and laundry detergent bottles.
- Symbol 5 – Polypropylene, PP, used in products such as pill bottles, yogurt cups and plastic utensils.
However, these aren’t accepted in some facilities for reasons I’ll explain.
Taking apart plastics, bead by bead
Some plastics can be chemically recycled or ground up for reprocessing, but not all plastics play well together.
Simple separation methods, such as placing ground-up plastics in water, can easily remove your soda bottle plastic (PET) from the mixture. The ground-up PET sinks in water due to the plastic’s density. However, HDPE, used in milk jugs, and PP, found in yogurt cups, both float, and they can’t be recycled together. So, more advanced and expensive technology, such as infrared spectroscopy, is often required to separate those two materials.
Once separated, the plastic from your soda bottle can be chemically recycled through a process called solvolysis.
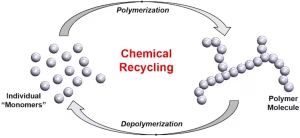
It works like this: Plastic materials are formed from polymers. A polymer is a molecule with many repeating units, called monomers. Picture a pearl necklace. The individual pearls are the repeating monomer units. The string that runs through the pearls is the chemical bond that joins the monomer units together. The entire necklace can then be thought of as a single molecule.
During solvolysis, chemists break down that necklace by cutting the string holding the pearls together until they are individual pearls. Then, they string those pearls together again to create new necklaces.
Other chemical recycling methods, such as pyrolysis and gasification, have drawn environmental and health concerns because the plastic is heated, which can release toxic fumes. But chemical recycling also holds the potential to reduce both plastic waste and the need for new plastics, while generating energy.
The problem of yogurt cups and milk jugs
The other two common types of recycled plastics − items such as yogurt cups (PP) and milk jugs (HDPE) − are like oil and water: Each can be recycled through reprocessing, but they don’t mix.
If polyethylene and polypropylene aren’t completely separated during recycling, the resulting mix can be brittle and generally unusable for creating new products.
Chemists are working on solutions that could increase the quality of recycled plastics through mechanical reprocessing, typically done at separate facilities.
One promising mechanical method for recycling mixed plastics is to incorporate a chemical called a compatibilizer. Compatibilizers contain the chemical structure of multiple different polymers in the same molecule. It’s like how lecithin, commonly found in egg yolks, can help mix oil and water to make mayonnaise − part of the lecithin molecule is in the oil phase and part is in the water phase.
In the case of yogurt cups and milk jugs, recently developed block copolymers are able to produce recycled plastic materials with the flexibility of polyethylene and the strength of polypropylene.
Improving recycling
Research like this can make recycled materials more versatile and valuable and move products closer to a goal of a circular economy without waste.
However, improving recycling also requires better recycling habits.
You can help the recycling process by taking a few minutes to wash off food waste, avoiding putting plastic bags in your recycling bin and, importantly, paying attention to what can and cannot be recycled in your area.![]()
Alex Jordan is an associate professor of plastics engineering at the University of Wisconsin-Stout.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article. Banner photo: Plastic waste collected for recycling (iStock image).




Wow, this is the most thorough guide to recycling Ive ever read, from the initial sorting chaos to the chemical wizardry of solvolysis! It’s fascinating that plastic soda bottles (PET) are so easily separated from milk jugs (HDPE) – turns out they dont even get along in water! But then, the real humor lies in realizing my yogurt cup (PP) and milk jug (HDPE) are basically oil and water, making their reprocessing a never-ending battle of flexibility versus strength. The compatibilizer solution sounds like adding a dash of magic lecithin to make them play nicely, which is brilliant! Though I suspect my plastic bags (LDPE, symbol 4) might just be hiding under the couch, refusing to follow any rules. Overall, a fantastic dive into the messy, complex, and surprisingly funny world of plastic recycling!quay random